The Nguyen Dynasty (Nôm: 茹阮, Han: 阮朝; Sino-Vietnamese: Nguyen Trieu) was the last feudal dynasty of Vietnam, established and ruled by the powerful Nguyễn family. The Nguyen Dynasty rose to power from the 16th century until the mid-20th century (1802 – 1945). Spanning 143 years of existence, the Nguyen Dynasty witnessed numerous ups and downs in history, particularly the French invasion in the mid-19th century. Let’s take a look back at the historical process of the Nguyen Dynasty, one of the most prominent dynasties in Vietnamese history, in this article!
Table of Contents
When was the Nguyen Dynasty established?
The Nguyen Dynasty (1802 – 1945) was established in 1802 after Emperor Gia Long ascended to the throne. The Nguyen Dynasty was also the last feudal dynasty in the history of Vietnam. From 1802 to 1804, the dynasty used the national name Nam Viet, from 1804 to 1839 it used the national name Viet Nam, Dai Viet Nam, and in 1839, Emperor Minh Mang changed the national name to Dai Nam. The Nguyen Dynasty marked many ups and downs in history, particularly the French invasion in the 19th century.
The ancestors of the Nguyen Dynasty kings were the Nguyen lords during the Trinh-Nguyen rivalry period. Nguyen Phuc Anh (Gia Long) was the first emperor of the Nguyen lineage, and he proclaimed himself emperor in 1802. Nguyen Phuc Anh was the grandson of Lord Nguyen Phuc Khoat, the last Nguyen lord in the central region. After the Nguyen lord family was overthrown by the Tây Sơn – Nguyen Hue forces in 1777, he fled and began a 25-year war against the Tây Sơn. Nguyen Anh sought the assistance of the French and the Qing Dynasty troops, weakening the Tây Sơn forces.
After the sudden death of King Quang Trung, Nguyen Anh maintained control over the southern region and in 1802 completely defeated the Tây Sơn, becoming emperor and establishing the Nguyen Dynasty with the country’s name as Viet Nam, choosing Phu Xuan (Hue) as the capital. The Nguyen Dynasty was a dynasty marked by many ups and downs in history, including the French colonization in the 19th century.

In 1802, the descendant of the Nguyen family, Nguyen Anh, overthrew the Tây Sơn Dynasty and established the Nguyen Dynasty. In the early period of their rule, they attempted to consolidate unified governance and promote urgent reforms and cultural development. However, the Nguyen Dynasty failed to modernize the country, and when the French colonialists invaded, they quickly surrendered, while people throughout Vietnam rose up to resist the invaders.
When did the Nguyen Dynasty come into being?
The Nguyen Dynasty came into being in the context of the post-Trinh-Nguyen rivalry period, which took place from 1593 to 1778. In 1777, Nguyen Anh (Nguyen Phuc Anh), the descendant of the Nguyen lords in the southern region, escaped from the persecution by the Tây Sơn forces. He lived in exile in Siam (now Thailand) and endured hardships for 25 years, nurturing a strong determination to seek revenge against the Tây Sơn and defeating their loyalist forces.
After the death of King Quang Trung, the Tay Son dynasty gradually weakened. Taking advantage of this opportunity, Nguyen Anh mobilized his forces to attack the Tay Son dynasty with the assistance of Siam and France. In 1802, Nguyen Anh concentrated his forces to conquer the southern region, and then defeated the Tay Son dynasty, establishing the unified Nguyen Dynasty that ruled over a vast territory from the south to the north. The Tay Son dynasty was overthrown, and Nguyen Anh ascended the throne as Emperor Gia Long, with the capital established in Phu Xuan (Hue).
Nguyen Anh and Le Chieu Thong were the only two kings who sought the assistance of foreign powers to overthrow the existing dynasty, seize the throne, and govern the country. Therefore, in history, there have been differing opinions about Nguyen Anh’s actions.
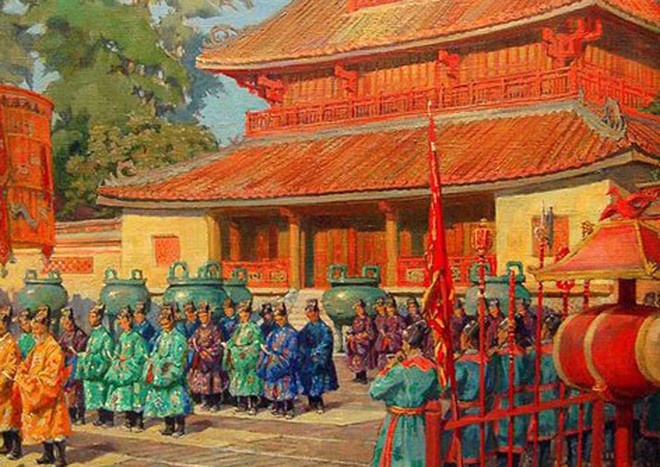

In the world, the early 19th century was a time when capitalism was flourishing, with political systems tending to be more democratic. In Vietnam, however, the feudal Nguyen Dynasty came into being. It was the last monarchy in the history of Vietnam’s feudal rule, which ended in 1945 with the successful August Revolution during the reign of King Bao Dai.
Emerging in a unique context, the Nguyen Dynasty went through many upheavals during its existence. It faced challenges such as seeking assistance from foreign powers, losing sovereignty to French colonization, but also made significant contributions to the unification of the country, territorial expansion, and economic development. Therefore, when evaluating this dynasty, a fair and objective assessment is needed to understand its role in the history of Vietnam.
The two main periods of the Nguyen Dynasty’s history.
The first period (1802-1858) is the period of independence and self-governance.
The Nguyen kings held full control over the country, spanning four reigns: Gia Long, Minh Mang, Thieu Tri, and Tu Duc. The Nguyen kings in this period sought to build Vietnam based on Confucianism and abolished the progressive reforms of the Tay Son dynasty.
During the reign of Minh Mang, there were numerous wars in Cambodia to expand territory, which depleted the treasury. By the time of Tu Duc, all aspects of the country were in decline. In the 1850s, a portion of Vietnamese intellectuals, exemplified by Nguyen Truong To, recognized the stagnation of the country and advocated for learning from the West to develop industry and commerce, as well as reforming the military and foreign affairs.
However, most of the Nguyen court officials and scholars failed to perceive the necessity of reforms and opening up the country, so Tu Duc lacked determination to implement these proposals. Dai Nam gradually became stagnant, backward, and at risk of European colonial invasion.
The second period (1858-1945) is the period of French colonization and domination.
It began when the French troops attacked Da Nang and ended with Emperor Bao Dai’s abdication in 1945.
In August 1858, the French naval forces attacked the port of Da Nang and then advanced to capture Gia Dinh (Saigon). In June 1862, King Tu Duc signed a treaty ceding three eastern provinces to France.
In 1867, France occupied the three western provinces, forming the colony of Cochinchina. After consolidating their position in Cochinchina, from 1873 to 1886, the French waged wars in Tonkin (Northern Vietnam). Finally, in 1884, the Nguyen Dynasty officially recognized French rule over Vietnam.
The French held the ruling power over the country, while the Nguyen emperors maintained their imperial titles but acted as mere puppets. The French could establish puppet emperors from the Nguyen Dynasty at their discretion. This period ended when Bao Dai declared his abdication in 1945.
From 1883 onwards, the Vietnamese people continued their multifaceted struggle to protect their national cultural identity, selectively assimilate Western cultural values, and engage in a series of uprisings with various aims to expel colonialism, capitalism, and regain independence.
In 1930, the Indochinese Communist Party was founded, putting forth the correct Revolutionary line. Over 15 years, under the leadership of the Vietnamese people, the August Revolution of 1945 was carried out, overthrowing the colonial feudal regime, establishing the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, and ushering in a new era for the Vietnamese nation.
How many kings did the Nguyen Dynasty have?
The Nguyen Dynasty was the last imperial dynasty in the history of Vietnam, lasting for 143 years (1802-1945) and spanning 13 kings. The dynasty was established when King Gia Long (Nguyen Anh) ascended the throne in 1802 and ended with the abdication of Emperor Bao Dai in 1945.
The kings of the Nguyen Dynasty were:
- Gia Long (1802-1820)
- Minh Mang (1820-1840)
- Thieu Tri (1841-1847)
- Tu Duc (1847-1883)
- Duc Duc (3 days, 1883)
- Hiep Hoa (6 months, 1883)
- Kien Phuc (1883-1884)
- Ham Nghi (1884-1885)
- Dong Khanh (1885-1888)
- Thanh Thai (1889-1907)
- Duy Tan (1907-1916)
- Khai Dinh (1916-1925)
- Bao Dai (1926-1945)
The imperial capital Hue was built during the reign of which king? The history of the Imperial City of Hue.
In April 1805 (the year of At Suu), the Nguyen dynasty began the construction of the Imperial City. The Nguyen rulers mobilized over 30,000 soldiers and workers from Quang Binh to Quy Nhon to participate in the construction of the Imperial City of Hue. Various materials such as stone, wood, lime, bricks, and tiles were brought from all regions of the country. After several decades of construction and multiple renovations, a magnificent and vast citadel, stretching 2km, emerged on the banks of the Perfume River.
By 1807, an additional 80,000 soldiers from Thanh Nghe and Bac Thanh were brought in to reinforce the labor force day and night. Initially, the walls were made of soil, with outer facades covered in wooden planks. In the 17th year of Gia Long’s reign (1818), brick construction began on the western and southern sides. The eastern and northern sides were built with bricks in 1822. In 1832, during the reign of Minh Mang, the construction was completed, and subsequent renovations were carried out.
The location of the Imperial City of Hue was originally chosen by the Nguyen lords as the capital of the southern region from 1687 to 1775. Later, during the Tây Sơn dynasty, it served as the national capital from 1788 to 1801. King Gia Long selected this location again to build the Imperial City on a larger scale, situated on the land of eight villages: Phu Xuan, Van Xuan, Dien Phai, The Lai, An Van, An Hoa, An Buu, and An My.
The Imperial City was built in the style of Vauban, nearly square-shaped, covering an area of 520 hectares, with a circumference of over 10,500 meters. The fortification system, including the Imperial City (outer citadel), the Royal Enclosure, and the Forbidden Purple City (inner citadel), all aligned on one axis, facing south-southeast, was constructed based on the topography of Mount Ngu and the Perfume River. The main axis of this system runs through the middle of Ngu Binh mountain.
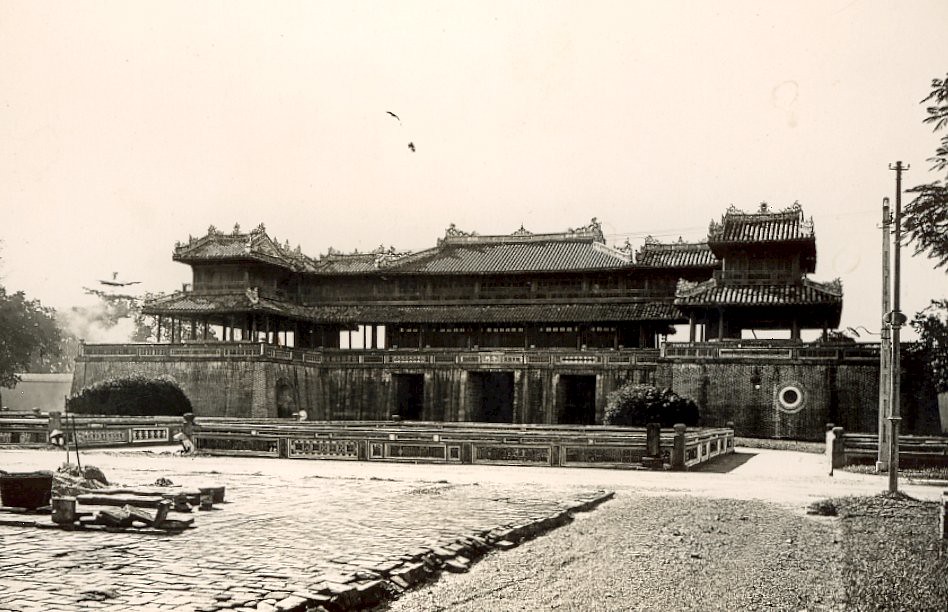

The Royal Enclosure was the most important political and administrative center of the dynasty, built in 1804 and completed and upgraded in 1833. It covered an area of 36 hectares, nearly square-shaped, with each side measuring about 600 meters. Within the Royal Enclosure, there are over 100 beautiful architectural structures divided into different areas, each serving specific functions.
The Imperial City of Hue holds significant defensive value. Surrounding the citadel walls are 24 fortresses, along with an auxiliary fortress called Tran Binh Dai (Small Mang Pond). All of these structures, combined with the Hồ Thành Ha (outer defensive wall), created a robust defensive system.
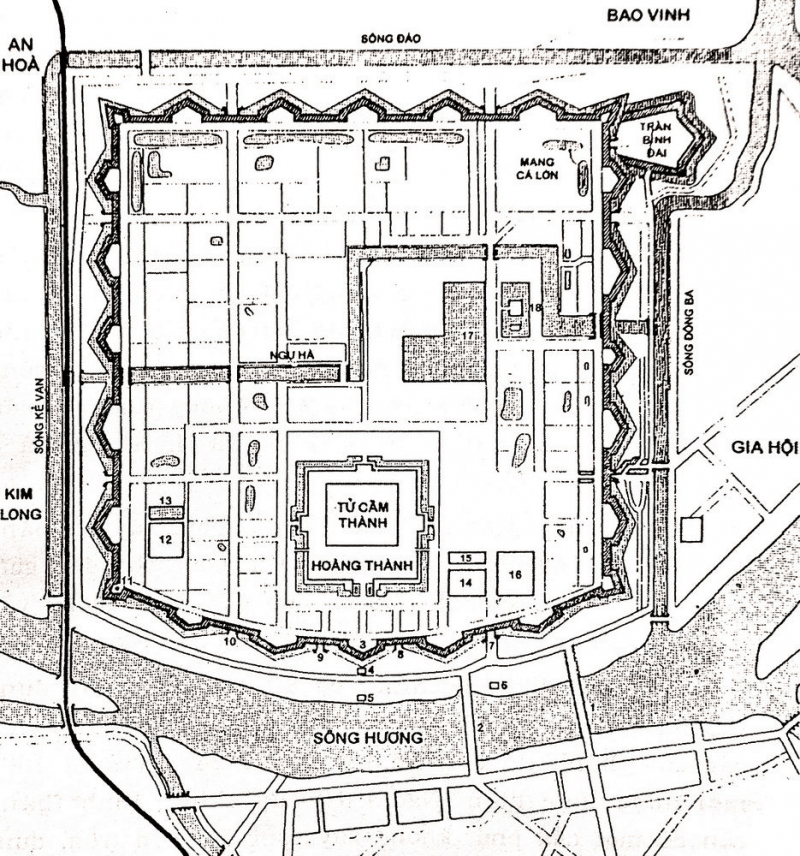
The architecture of the Imperial City of Hue is a harmonious and intelligent combination of architecture and nature. It represents the knowledge and craftsmanship of the Vietnamese people in the first half of the 19th century.
If you are planning to visit the ancient capital of Hue to explore the history and discover the tombs of the Nguyen Dynasty kings, please contact us for the best transportation services in Hue.
Policies and Governance of the Nguyen Dynasty
The Administrative Machinery of the Nguyen Dynasty
Bureaucratic System and Central Government Organization during the Nguyen Dynasty
The Nguyen Dynasty essentially maintained the same bureaucratic system and central government structure as the previous Le Dynasty. At the head of the state was the emperor, holding all the executive powers. To assist the emperor in handling paperwork, official documents, and recordings, there was the Van Thu Phong (later changed to Noi Cac in 1829). In terms of important military affairs, there were four Dai Hoc Si (Grand Doctorate) known as the Four Pillars of the Court, which later became the Institute of Confidentiality in 1834. Additionally, there was the Tong Nhan Phu responsible for the affairs of the Royal Court.
Below the imperial court, six Ministries were established, each headed by a Minister who was responsible for directing the general affairs of the state. The ministries included the Ministry of Rites, Ministry of Interior, Ministry of Ceremonies, Ministry of War, Ministry of Justice, and Ministry of Public Works. Alongside the six ministries, there was the Dosat Vien (also known as Ngusudai), consisting of six departments responsible for inspecting and supervising officials, and the Han Lam Vien, which handled various documents and communications. There were also five Tự (self-governing bodies) responsible for specific matters, the Nội Vụ Phủ overseeing treasury matters, the Quốc Tử Giám in charge of education, the Thai Y Vien responsible for healthcare and medicine, as well as several other offices and bureaus.
During the Nguyen Dynasty, the kings did not appoint a queen regnant and abolished the position of prime minister. They personally took direct control over important internal affairs from the central to local levels, including legislating laws, organizing Hoi examinations, making changes to key court officials, mobilizing distant military expeditions, and directly managing the local authorities. All these decisions were made by the kings themselves. This demonstrated that the Nguyen kings were not willing to share their power with anyone else.
Administrative Division during the Nguyen Dynasty.
In 1802, while deciding on Phu Xuan as the capital, Nguyen Anh temporarily established 11 trấn (equivalent to the present-day northern region) in the north as a Tổng Trấn (General Governorate) called Bac Thanh, led by a Tổng Trấn.
During the reign of Minh Mang, in order to unify the administrative units throughout the country, in 1831-1832, the king implemented a major administrative reform by abolishing the Tổng Trấn system and transforming dinh and trấn into provinces. This was the first appearance of provincial administrative units in Vietnam.
The provinces were headed by Tổng Đốc (Governor-General) who was in charge of 2-3 provinces and a Tuần Phủ (Deputy Governor) who was responsible for a single province. The administrative tasks were divided between Bố Chánh Sứ Ti (Fiscal and Administrative Affairs) responsible for taxation, household registration, and administration, and Án Sát Sứ Ti (Security and Legal Affairs) responsible for security and legal matters. Military affairs were overseen by a Lãnh Binh (Military Commissioner). The provincial officials were directly appointed by the central government, usually high-ranking military officials, and later supplemented by civilian officials. The governance system clearly distinguished between the central and local authorities, with the king, as the head of the country, holding significantly more power than in previous periods.
Below the province were phủ (prefectures), huyện (districts), châu (sub-districts), tổng (townships), and xã (communes). The imperial officials were only involved in the administration up to phủ huyện, while the selection of officials from tổng downwards was done by the local residents. Each tổng consisted of several villages or communes, with a cai tổng (township chief) and a deputy township chief appointed by the Council of Village Elders to manage taxation, infrastructure, and security within the tổng. In general, the administrative structure of the tổng and xã was tightly organized to facilitate effective governance and prompt response to any changes or incidents.
As of the end of the 19th century, Vietnam had 98 phủ (prefectures) consisting of 342 huyện (districts) and châu (sub-districts).
Regarding the two archipelagos of Hoang Sa (Paracel) and Truong Sa (Spratly), King Gia Long officially ordered the incorporation of Hoang Sa into Vietnam in 1816. The Vietnamese flag was planted on the islands, and hydrographic surveys were conducted. During the reign of Minh Mang, the Nguyen Dynasty constructed shrines, erected stone steles, installed markers, and planted trees on the islands. The Hoang Sa Flotilla and Bac Hai Flotilla were assigned additional tasks such as exploitation, patrol, collection of taxes from residents on the islands, and defense of the two archipelagos. These flotillas continued their operations until the arrival of the French in Indochina. From the 1890s, the protectorate authorities in the name of the Hue court of the Nguyen Dynasty planned to establish a lighthouse to assert French sovereignty over the Hoang Sa archipelago, but the project was not realized, and it was not until 1938 that an official force occupied these islands. However, when the Qing Dynasty sent ships to encroach upon the Hoang Sa archipelago in the early 20th century, the French Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a protest note. This dispute continued until the French lost their sovereignty in Indochina and has yet to be resolved.
The Nguyen Dynasty’s Military.
After gaining control of the entire country, the Nguyen Dynasty built a more sophisticated and disciplined military. To maintain a well-equipped army, King Gia Long implemented a recruitment system based on household registration, selecting 1 soldier from every 3, 5, or 7 households. The regular army was stationed in the capital and strategically weak areas, while localities had their own armed forces responsible for maintaining public order. The regular army consisted of 140,000 soldiers, in addition to auxiliary troops. The military was organized into four branches: infantry, cavalry, navy, and artillery, with a focus on developing the infantry and navy for independent operations. In addition to traditional weapons, the regular army was equipped with Western firearms such as muskets, rifles, steamboats, and explosives. Cannon and mortars were standardized in size and weight, and fortresses and small forts were regulated for each level with a certain number of troops.
Under Minh Mang’s rule, the Western model was adopted for organizing the military, aiming for a highly skilled and efficient army, reducing the number of flag bearers from 40 to 2 in a unit of 1 battalion (500 soldiers). The military tactics were observed by Manchu scholars to be similar to the French style, as Minh Mang’s army employed Western-trained officers. It can be said that during Minh Mang’s reign, the Nguyen Dynasty’s military was the most modern and advanced force in East Asia, surpassing neighboring countries such as China, Thailand, and Cambodia.

During the reign of Tu Duc, the defense efforts of the Nguyen Dynasty declined significantly, showing clear contrast with the previous reigns. One of the reasons for the military’s decline was financial issues. The modernization of weapons and equipment was almost nonexistent. The equipment for infantry was outdated: for every 50 soldiers, there were only 5 guns, and they only practiced shooting 6 rounds of ammunition once a year. The maintenance of weapons was also poor. In terms of the navy, no new warships were built, and the naval forces lacked the capability to protect the coast from pirates. The emphasis on Western military teachings diminished, returning to the Binh Thu Yeu Luoc (Essential Military Doctrine) of Tran Hung Dao. The living conditions of the soldiers were neglected, and their rations were reduced. As a result, the morale and fighting spirit of the soldiers were not high. The military philosophy of the Nguyen Dynasty’s rulers did not surpass the limits of feudal military science. The failure to keep up with the latest advancements in Western military science during Tu Duc’s reign caused Vietnam’s military to lag behind. Therefore, when the French invaded Vietnam in 1858, there was a significant gap in terms of equipment between the Nguyen Dynasty’s army and the French forces.
Tax and Labor Policies during the Nguyen Dynasty.
King Gia Long reorganized the issue of registration, requiring each village to record the number of men aged 18-60 in the village register.
Since Vietnamese society was fundamentally based on communal and village structures, the royal court did not directly demand taxes from the people. Instead, they delegated the task of tax collection and labor conscription to the villages, without specifying how the responsibilities would be divided among the villagers. Each village enjoyed a significant degree of self-governance, ruling according to their own customs recorded in the village’s regulations.
Regarding personal and land taxes, the Nguyen Dynasty abolished the previous tax system established by the Tay Son Dynasty and replaced it with a new, heavier tax regime. King Gia Long rectified the household registration records and land surveys that had been damaged during the internal conflicts. The household registration was divided into nine categories, and each category determined whether the entire tax was to be paid, or if exemptions or reductions would be granted for both tax collection and labor conscription.
During the reign of Minh Mang, the land tax was revised, and the country was divided into three regions for taxation purposes. According to the statistics of the Ministry of Interior, the population at the beginning of Gia Long’s reign was 992,559 people, and by the end of Thieu Tri’s reign, it was 1,024,380 people. As for land, Tự Đức’s reign started with 3,398,584 acres of cultivated land and 502,672 acres of uncultivated land.
Legal System during the Nguyen Dynasty.
Initially, the Nguyen Dynasty did not have a clear and detailed legal system. King Gia Long only ordered officials to refer to the Hong Duc Code to establish the 15 most important laws. In 1811, under Gia Long’s command, Nguyen Van Thanh, the governor of Bac Thanh, presided over the compilation of a new legal code, which was then promulgated by King Gia Long in 1815 under the name Hoang Viet Law or Gia Long Law. The Gia Long Law consisted of 398 articles divided into 7 chapters and was recorded in a set of 22 books that were printed and distributed everywhere. According to the preface, the law was developed by referring to the Hong Duc Code and the Qing Dynasty’s law, but in reality, it was almost a direct copy of the Qing Dynasty’s law with minor modifications. The chapter “Criminal Law” accounted for a significant portion, with 166 articles, while other chapters like “Family Law” had 66 articles, and “Administrative Law” had only 10 articles. The legal code included some strict laws, especially regarding acts of rebellion and spreading “subversive” speech or writing. However, the legal code also emphasized the fight against corruption and introduced many strict laws to punish corrupt officials. Of course, in the reigns of subsequent kings after Gia Long, this legal code was further revised and improved, especially during Minh Mang’s reign.
Foreign Policy during the Nguyen Dynasty.
Foreign policy with China:
Similar to previous dynasties, the first country with which Gia Long conducted diplomatic relations was China. In 1803, Gia Long sent envoys to China to request recognition of his royal title and investiture. In 1804, the Qing Dynasty sent envoys to confer the royal title on Gia Long. Since then, the Nguyen Dynasty had to regularly pay tribute to China.
Foreign policy with Cambodia and Laos:
Regarding Cambodia and Laos, the Nguyen Dynasty used military force to subjugate them, and at times, even established a protectorate over Cambodia.
Foreign policy with the West:
In the early stage, Gia Long pursued a relatively open policy towards France and Christian missionaries. However, during Minh Mang’s reign (1820-1840), the Nguyen Dynasty implemented a policy of suppressing Catholicism and closing off the country, aiming to prevent the influence of Westerners on Vietnamese soil.
The Nguyen Dynasty became increasingly conservative, leading the country to stagnation and backwardness to the point of losing the ability to defend itself.
The Nguyen Dynasty implemented a policy of religious prohibition against which religion?
The Nguyen Dynasty implemented a policy of religious prohibition against Catholicism. As early as the 17th century, when they began to look towards the East, the missionary activities of the Paris Foreign Missions Society became closely associated with French colonialism. The missionaries saw their missionary work as a precursor to a subsequent colonial invasion. Recognizing this danger, the Nguyen kings implemented a policy of religious prohibition against Catholicism.
From 1862, especially from 1874, due to various reasons stemming from the war with France, the Nguyen court created opportunities for the development of Christianity. The treaties of 1862 stipulated: “French and Spanish citizens may freely practice their religion in Vietnam, and the citizens of this country are allowed to convert to Christianity voluntarily without obstruction.” In 1865, Emperor Tu Duc issued an official decree granting freedom to the missionaries to spread their faith and allowing the people to freely adopt the religion. In 1874, according to the treaty, Catholics were granted the freedom to participate in examinations organized by the court and to engage in the state apparatus at all levels, participating in the country’s political and social activities as ordinary citizens.
Therefore, unlike the three traditional religions of Confucianism, Buddhism, and Taoism, which were trusted by the early Nguyen kings, Christianity faced frequent difficulties. However, due to conflicting interests and cultural disruptions, the prohibition order was consistently issued. Because of the strong anti-Christian sentiment and the presence of subversive elements, espionage, and those who exploited religion for political activities, Catholicism became a tool for invaders. By 1874, Catholicism had become openly active and gradually developed.
The anti-Nguyen dynasty uprising movements
The Nguyen dynasty attempted to perfect its ruling apparatus to stabilize the social situation but failed to prevent the development of corrupt practices.
The struggle movements erupted immediately after the establishment of the Nguyen dynasty and continued persistently. In the first half of the 19th century, there were nearly 400 uprisings against the Nguyen dynasty, averaging about 10 uprisings per year. During the reign of Emperor Minh Mang, a period of Nguyen dynasty’s development, there were 250 major and minor uprisings.
The struggle movements attracted participation from various social classes, and many uprisings were led by officials of the Nguyen dynasty, with even soldiers opposing the royal court.
The scale of the struggle movements spanned across the country, from the North to the South, occurring continuously and carrying strong local sentiments, but they did not form a unified movement. Therefore, the Nguyen dynasty had the opportunity to concentrate its forces for suppression.
Some notable uprisings against the Nguyen dynasty include:
- Phan Ba Vanh Uprising (1821-1827)
- Nong Van Van Uprising (1833-1835)
- Le Van Khoi Uprising (1833-1835)
- Cao Ba Quat Uprising (1854-1856)
In addition, in the southern region (Nam Ky), the incompatible policies of the Nguyen dynasty towards minority groups, especially the Khmer people, and the foreign policy towards the Kingdom of Champa, also caused dissatisfaction among the Khmer community, leading to numerous uprisings against the royal court, such as the Lam Sam, Ba Xuyen, That Son, and Ha Tien uprisings.
The downfall of the Nguyen Dynasty marked the end of its 143-year existence.
After the death of Gia Long in 1820, the Nguyen Dynasty adopted a conservative policy opposing foreign missionary activities in Vietnam. The French, partly due to this anti-missionary policy, invaded Vietnam in 1858, initially landing in Da Nang and later establishing a base in Saigon. They forced Emperor Tu Duc, who was already facing uprisings in other places, to cede three provinces in the eastern part of Cochinchina, known as French Cochinchina, in 1862. Five years later, the French gained control over the entire Cochinchina region. French control over all of Vietnam was established after invasions in 1883-1885, and Vietnam’s ancient vassal relationship with China came to an end. However, the Nguyen Dynasty retained its rule in Hue with nominal control over Central Vietnam, referred to by the French as Annam, and the northern part of Vietnam, known as Tonkin (Bac Thanh). The French continued their governance until 1945.

In August 1945, following Japan’s unconditional surrender to the Allies, the opportunity arose, and the Communist Party of Vietnam raised the flag of rebellion. The August Revolution took place within 15 days and was bloodless, yet it achieved independence and sovereignty after nearly a century of oppression. It also sounded the bell for the feudal history of Vietnam. On August 25, 1945, at the Gate of Noon, Bao Dai, the 13th and final emperor of the Nguyen Dynasty, read the Abdication Edict. On the afternoon of August 30, 1945, Bao Dai handed over the imperial seal to the revolutionary government. On September 2, 1945, President Ho Chi Minh read the Declaration of Independence, giving birth to the Democratic Republic of Vietnam.
Cultural heritage and symbols of the Nguyen Dynasty.
The Nguyen Dynasty left behind a significant cultural heritage for the Vietnamese people. Some of these have been recognized by UNESCO as world heritage sites, such as Hue Court Music (Nha Nhac), the Complex of Hue Monuments, and the Nguyen Dynasty Woodblocks.
Professor of history Phan Huy Le remarked, “No other period in Vietnamese history has left the nation with three cultural heritages recognized and honored by the world with such global significance.”
The Nguyen Dynasty also left behind an extensive archival system documenting its reign, an educational system, and thousands of communal houses, shrines, and temples spanning from the south to the north. Many of these cultural treasures have long been forgotten and considered as “remnants of a decaying dynasty.” Hue Court Music was recognized by UNESCO as an intangible cultural heritage representative of humanity in 2003.


Comments